Programming Mode
Application Area:
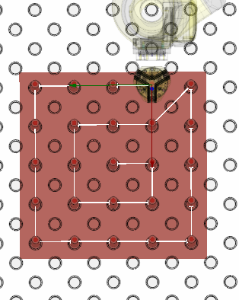
Programming Mode represents the pivotal operational environment in which theoretical plans are executed and robotic systems become operational. It functions as a multifaceted control center—a dedicated workspace for automation management and system configuration.
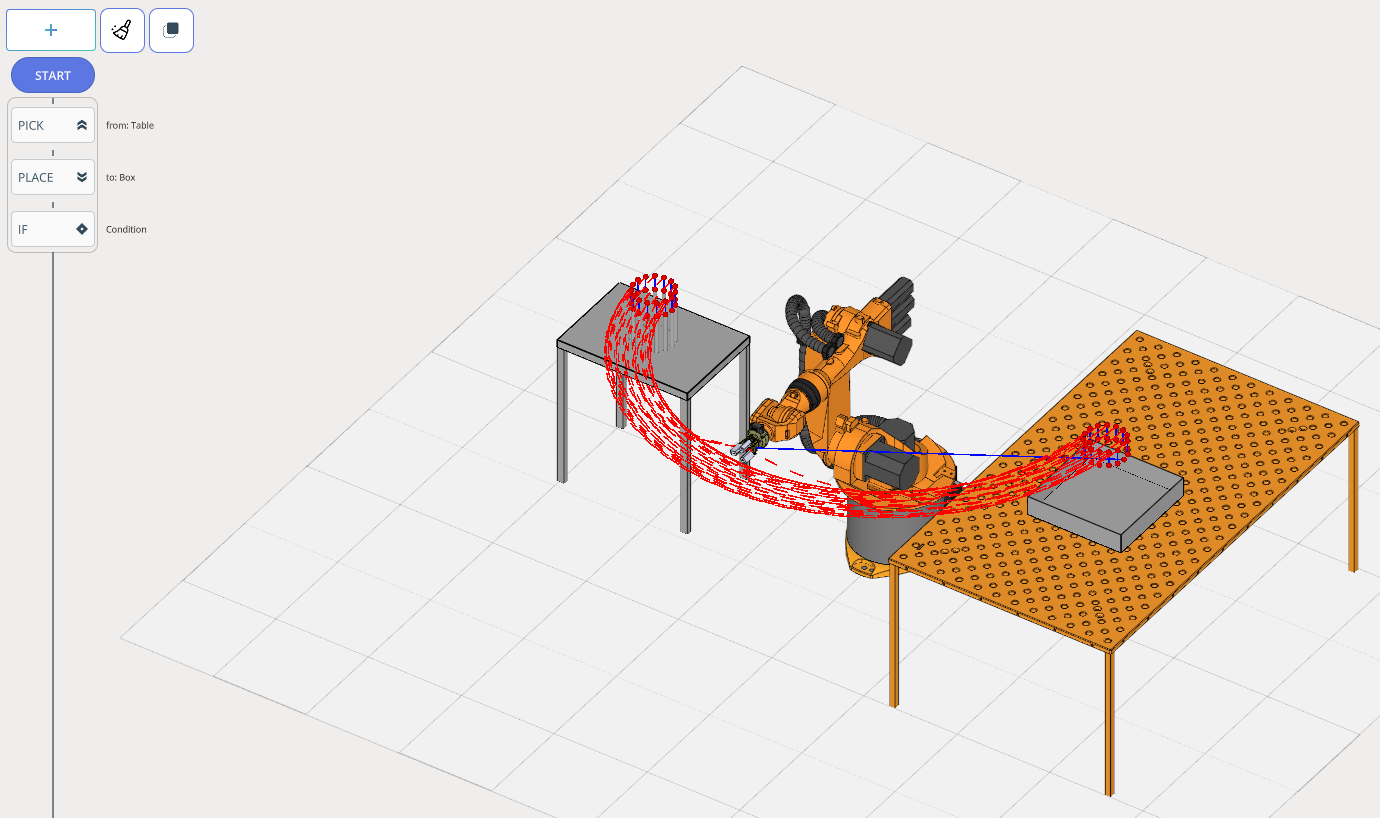
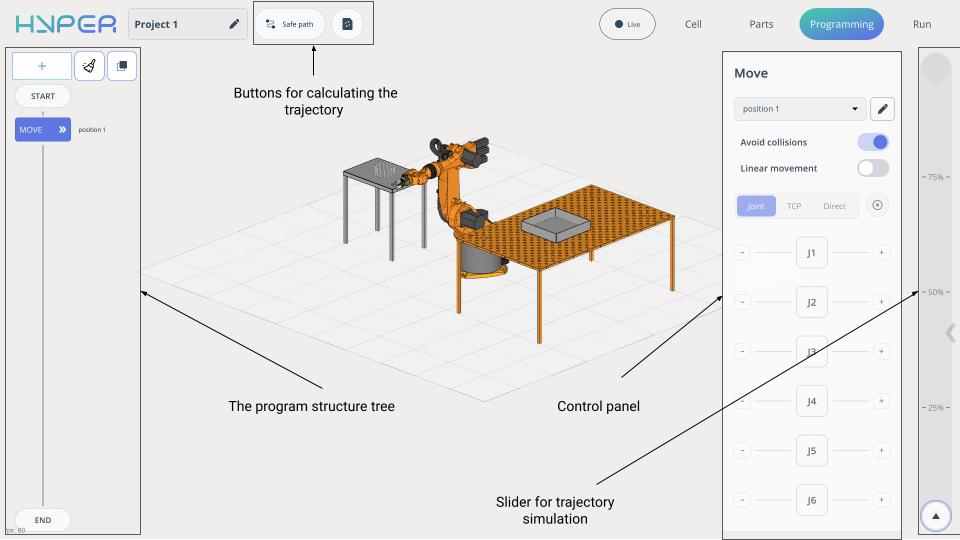
In Programming Mode, the Control Panel shifts to the right side of the screen and the Program Structure Tree is added.
Buttons for calculate the trajectory.
Quick calculation button. Calculates the trajectory without considering the checkboxes in collision avoidance commands.
Safe
Path
button. Computes trajectory with collision avoidance — only for commands where the flag is enabled.
Slider for simulation.
Simulate trajectory (speed controlled by slider).
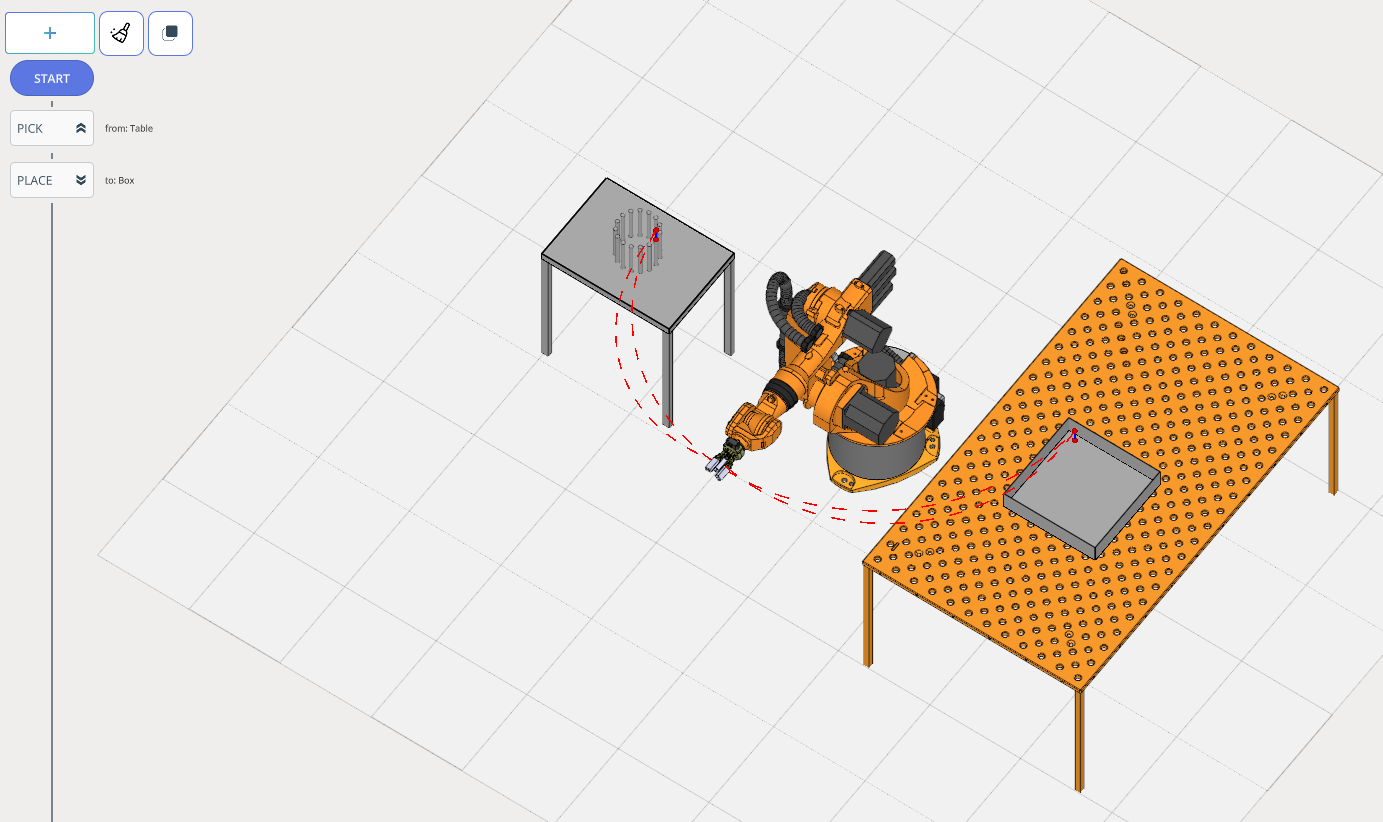
The Program Structure Tree consists of:
Buttons:
Add a command.
Allows you to add basic commands.

Clear.
To clear all commands and restart from the initial state.
![]()
Creates a Group.
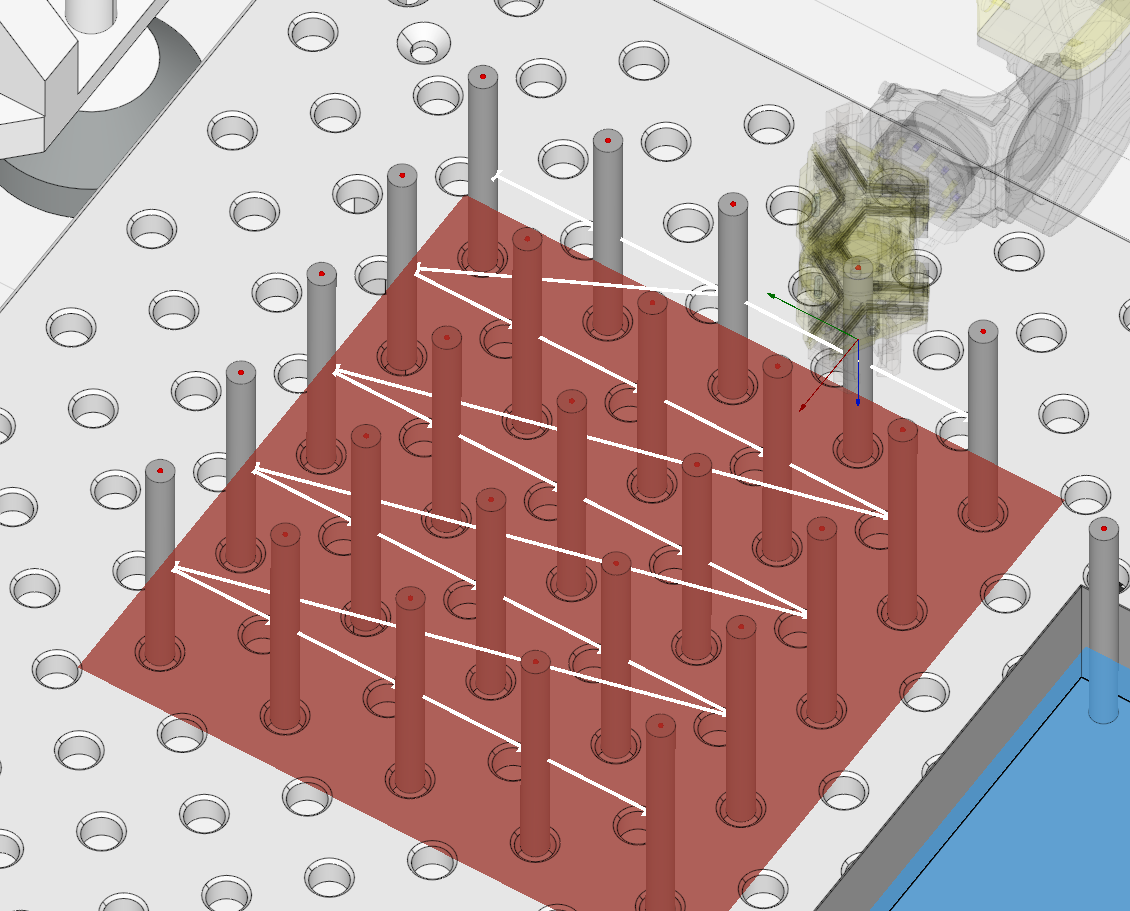
Commands can be organized into groups. Once created, a group can be copied, and the tray assignments for all commands in the group can be modified collectively. Efficient handling of repetitive tasks across multiple trays. ![]()
Commands:
Start . Set robot initial position. The Control Panel features navigation for robot movement in space. See more
End . Set robot final position. The Control Panel features navigation for robot movement in space. See more
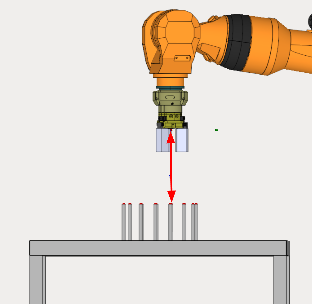
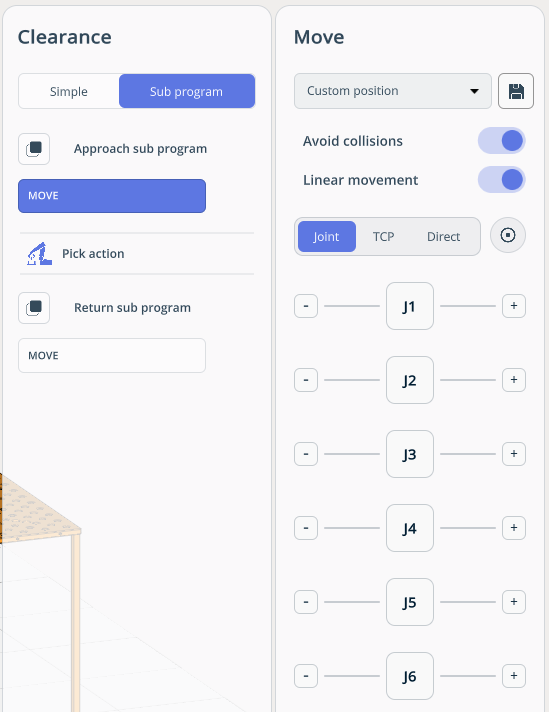
MOVE . Place robot at target position.
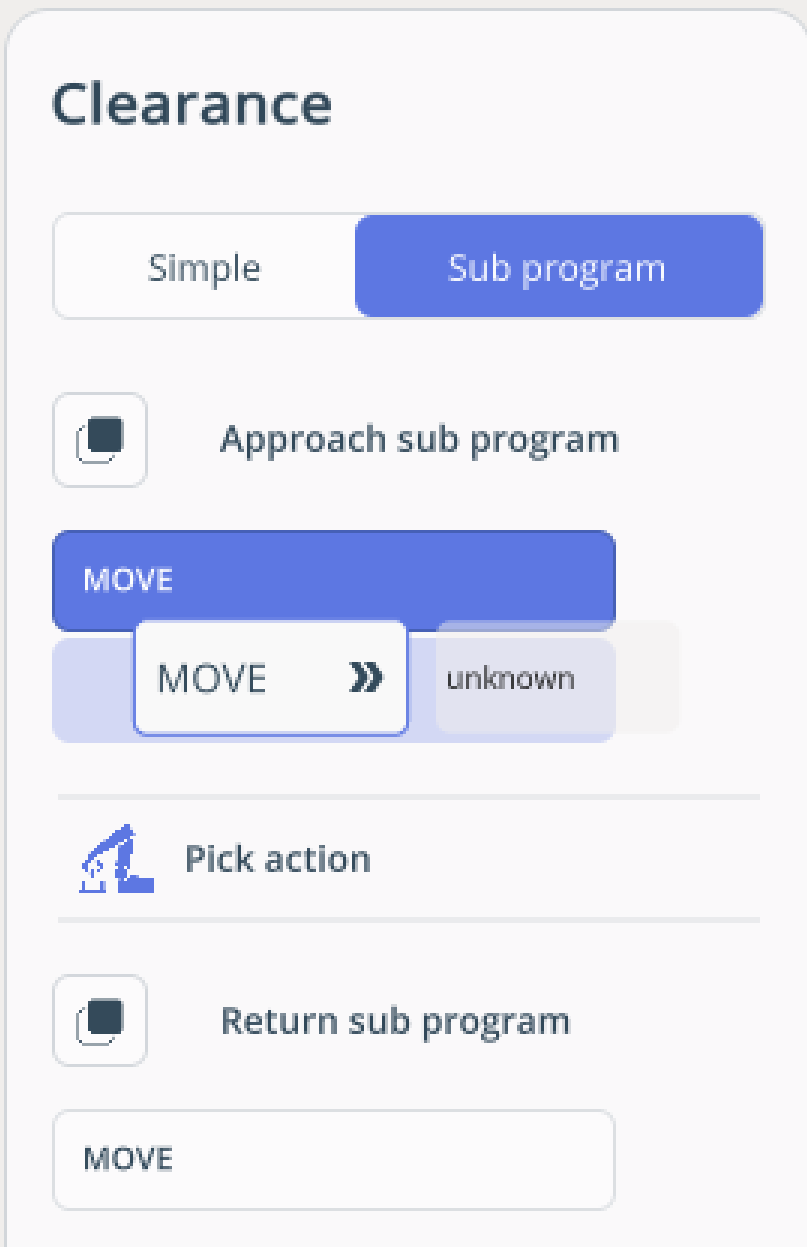
PICK/PLACE. Enables the robot to pick up/place a part.
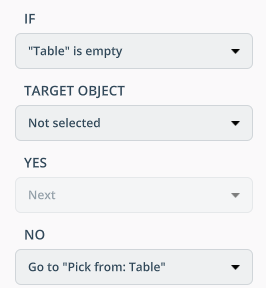
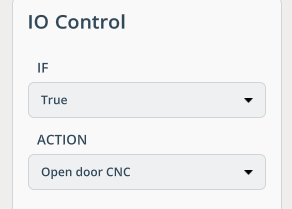
IF. Allows looping the program.
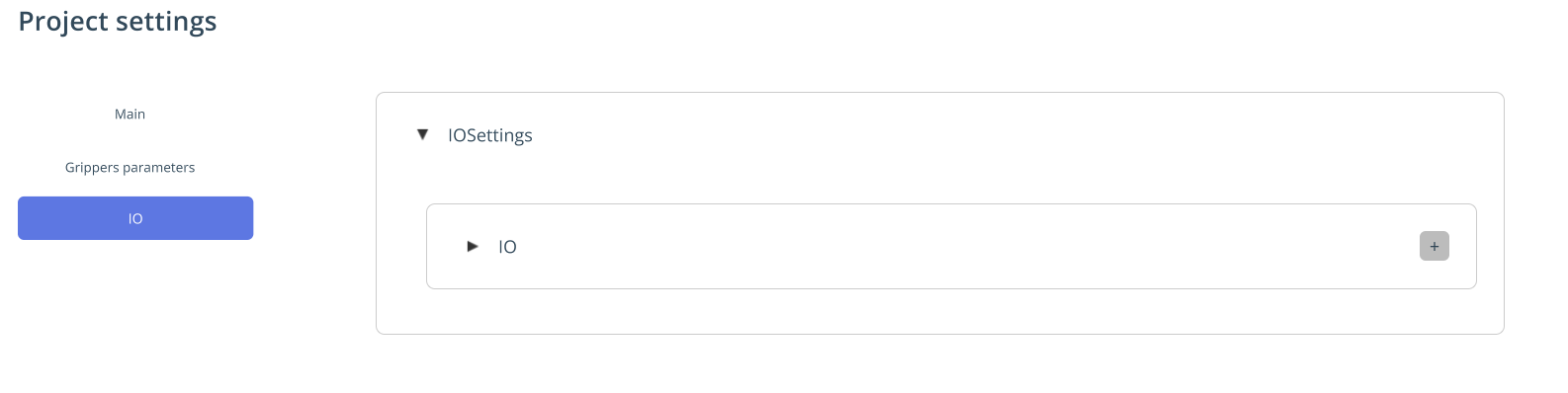
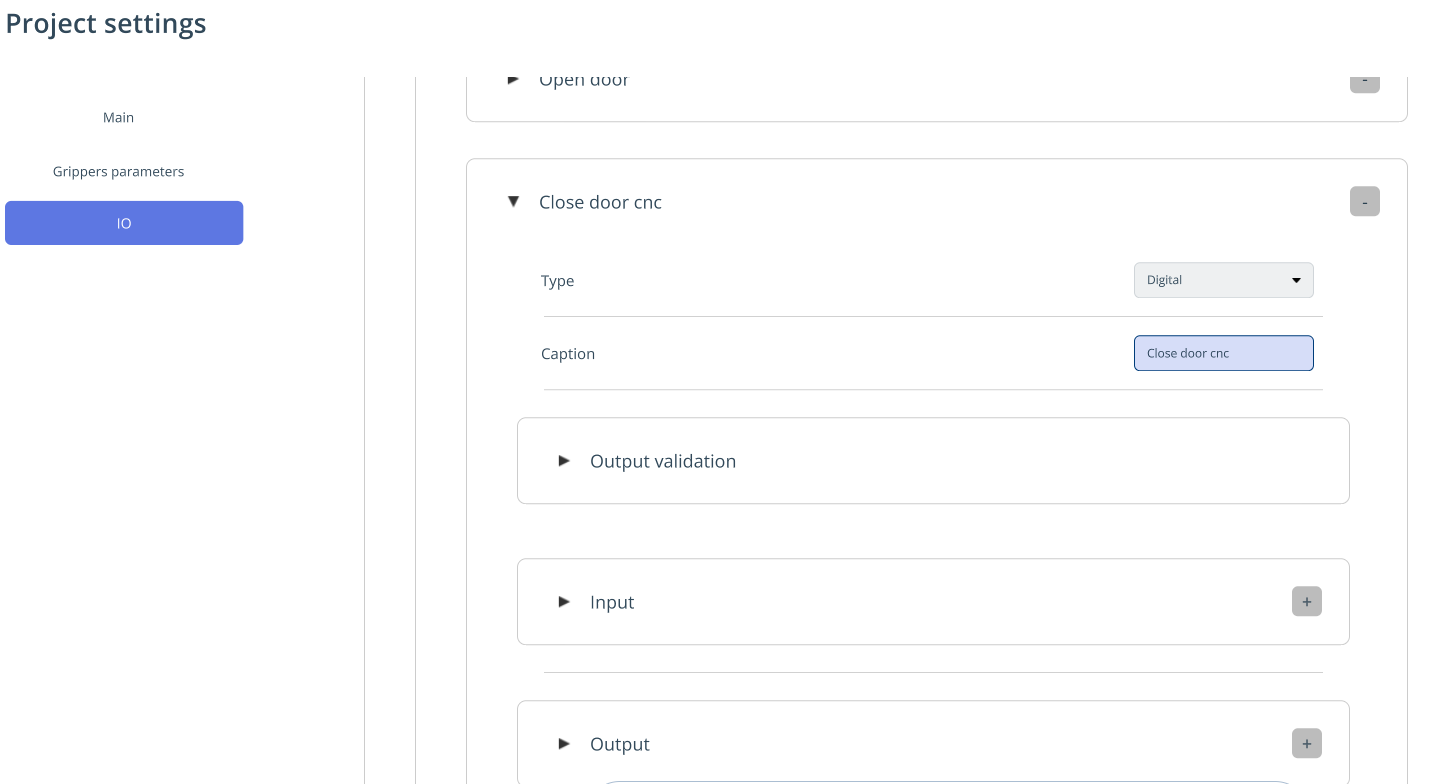
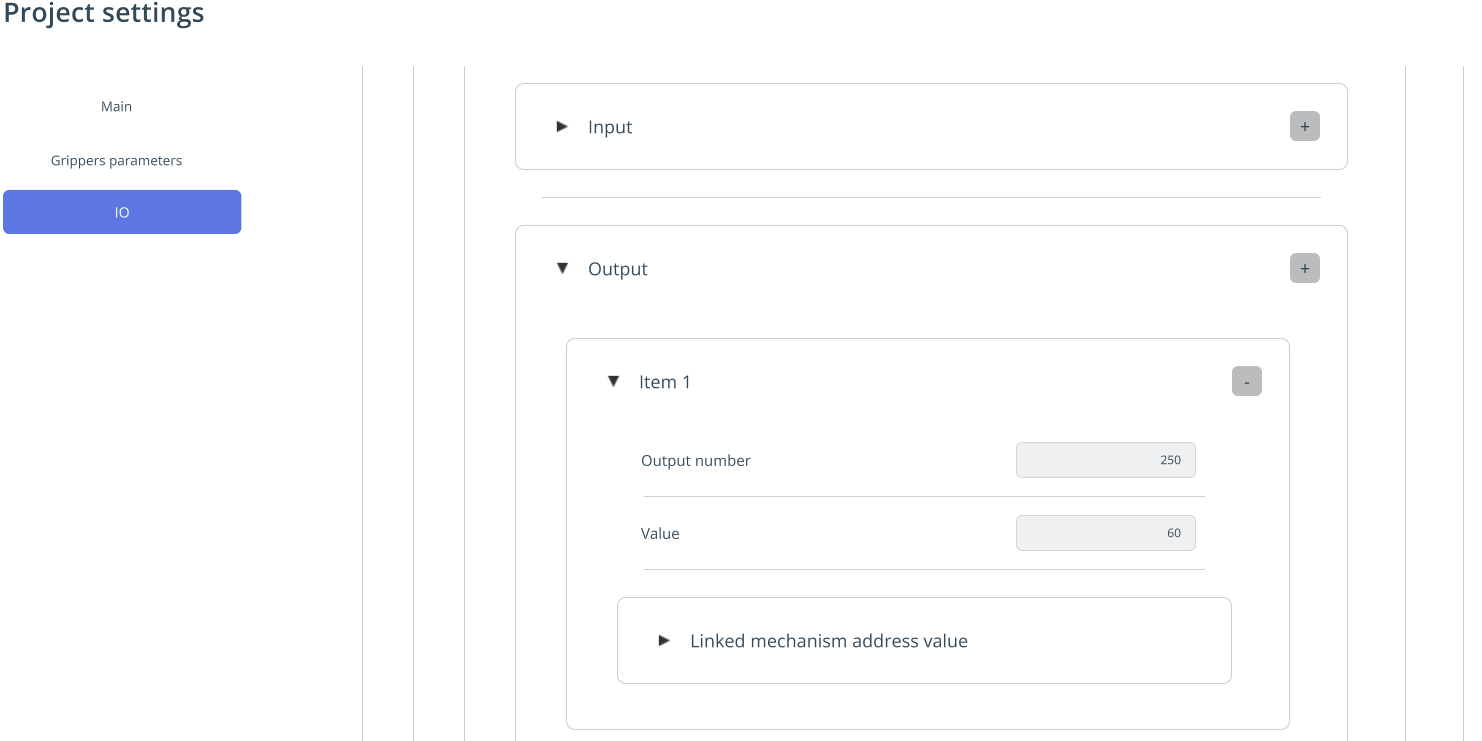
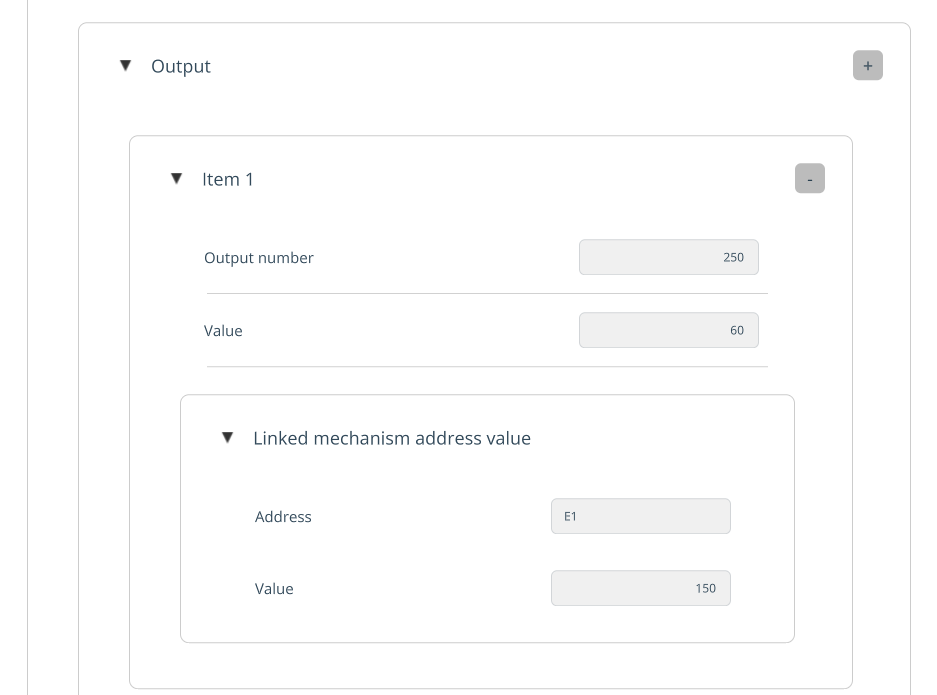
IO. This is required for managing inputs/outputs (external axes of machines and robots — machine doors, rails, etc.). IO is configured in Project Settings. See more
PAUSE. It allows you to set a delay between actions.
NAILING. The functionality is designed for nail driving.
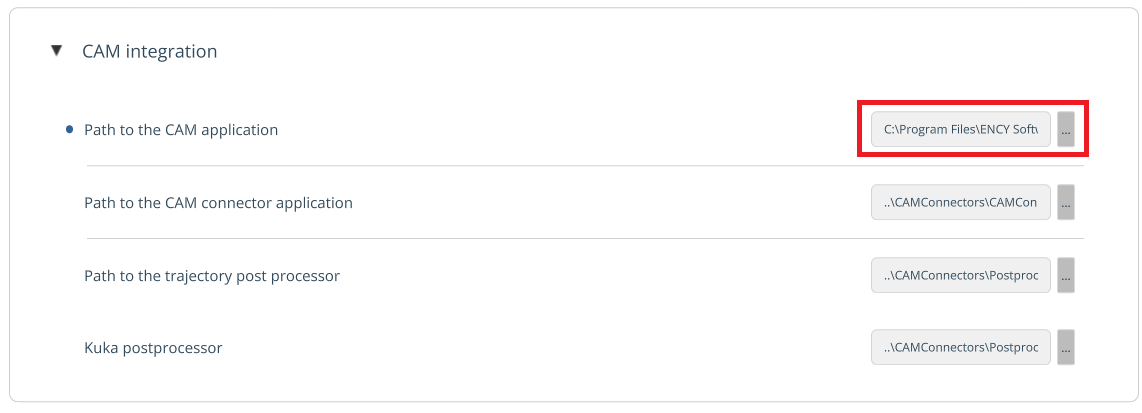
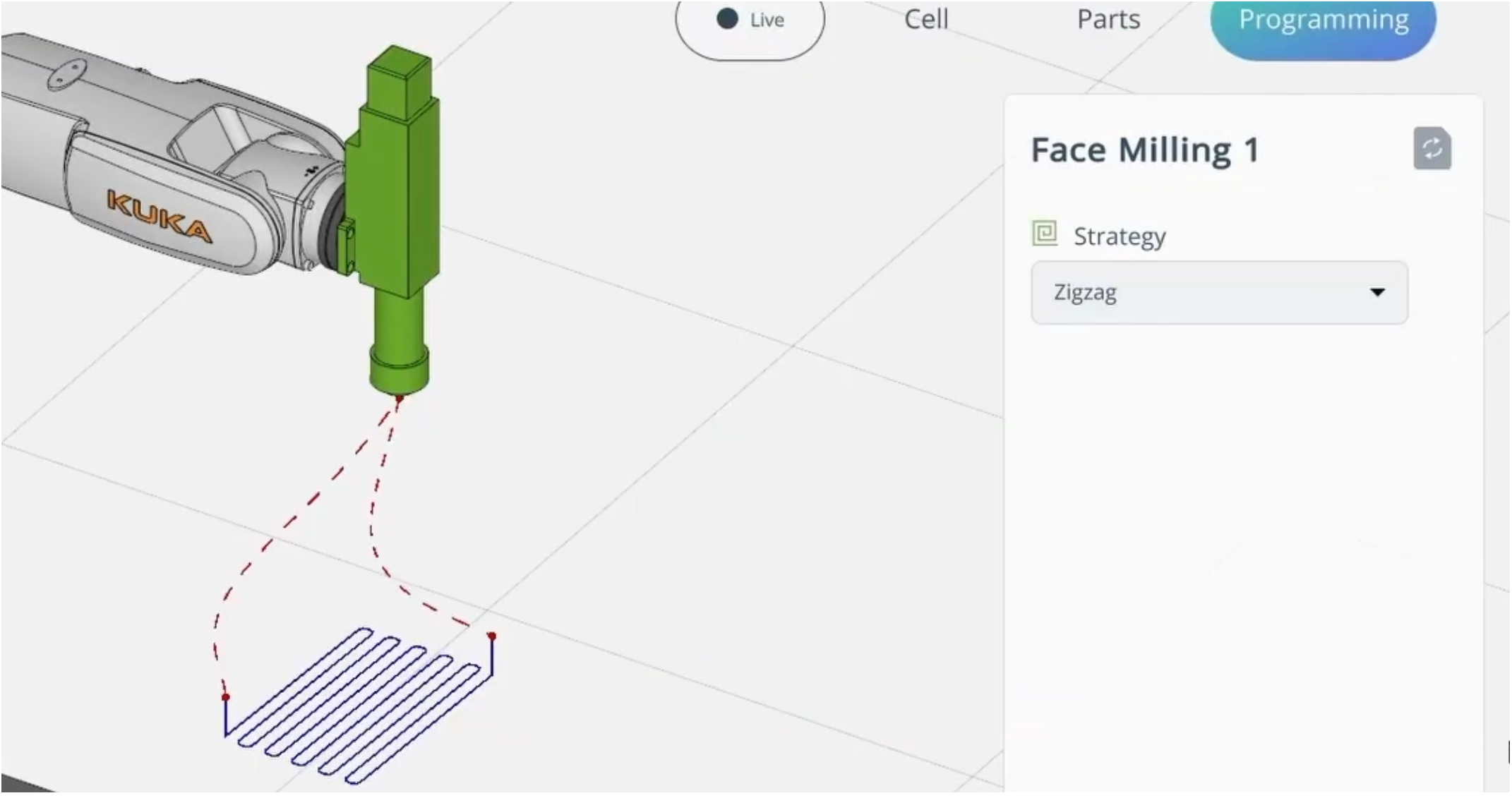
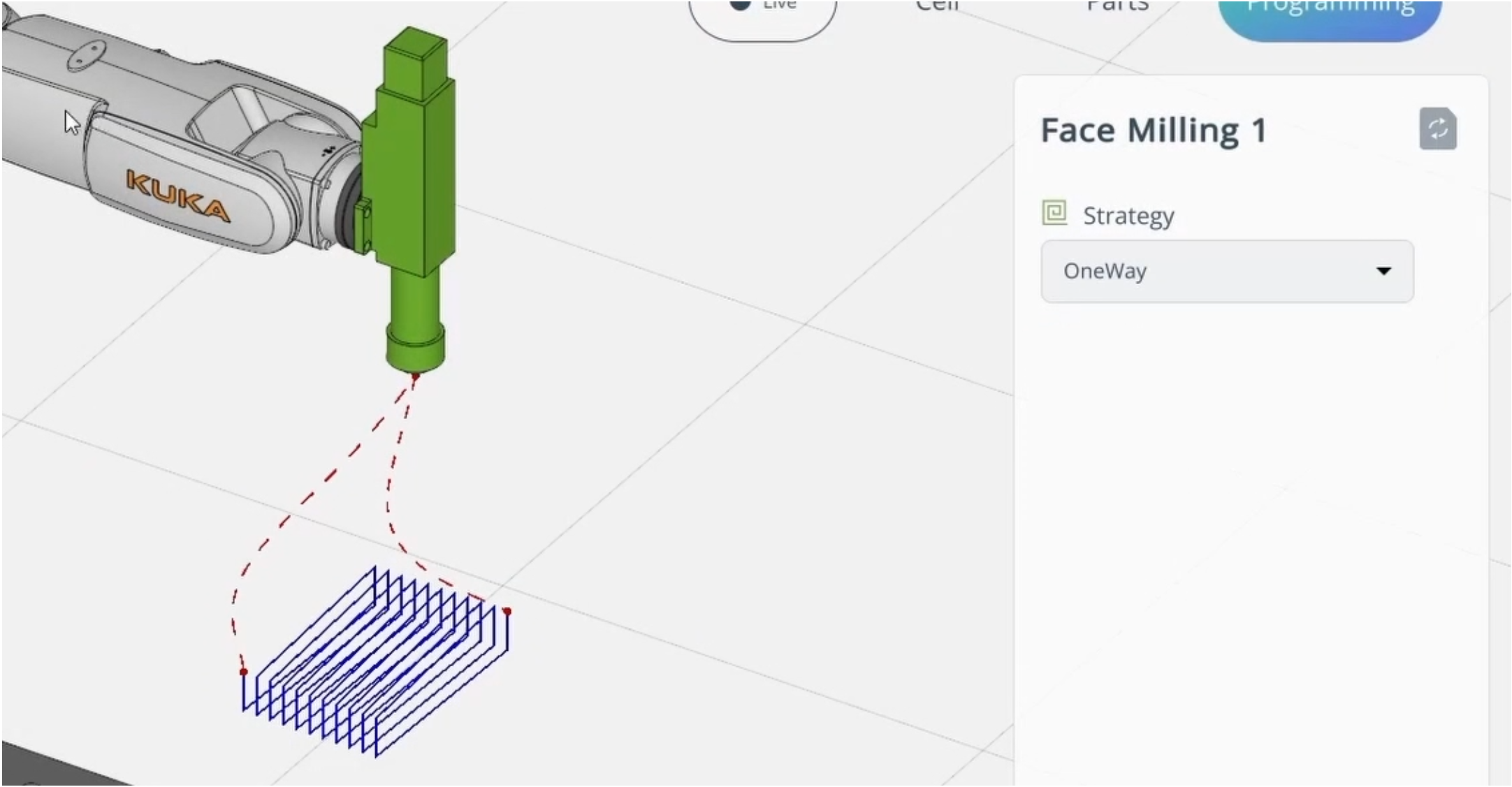
TRAJECTORY. It allows importing a trajectory from ENCY (CAM system).