Pocketing strategies
The pocketing strategies are designed for the removing of material in the open and closed pockets.
These strategies are available in the following operations:
Seven strategies are available to select in the Machining strategy drop-down:
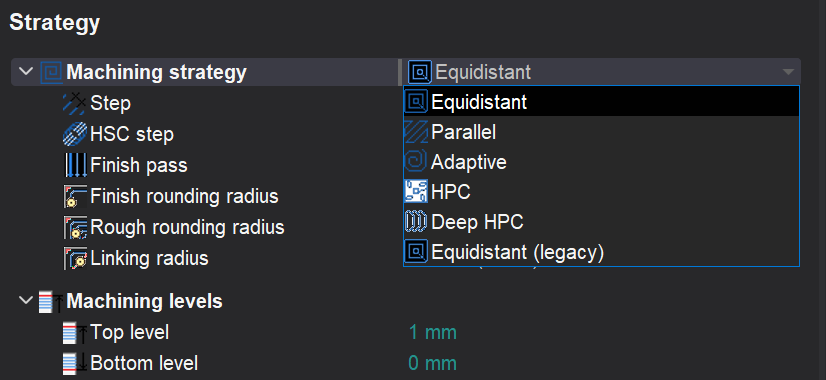
There are 6 strategies. Some items are optional and require an additional license. So many strategies are the result of long-term development. Every strategy has its own advantages and disadvantages, so no one of them can't be removed from the system.
|
Strategy |
|
|
|
Equidistant (legacy) |
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
|
Equidistant
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
|
HPC (high performance cutting)
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
|
Deep HPC
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
|
Adaptive
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
|
Parallel
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
Features of Adaptive strategy
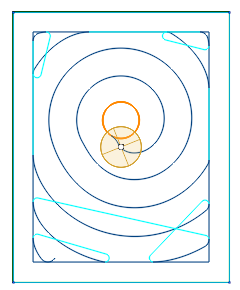
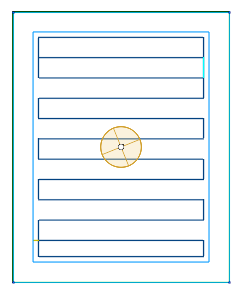
The strategy is used to effectively remove large volumes of material with high feed rates, maximal cutting depths (up to the flute's length) and relatively shallow cutting widths (5% to 30% of the tool diameter). Such parameters are possible as the specified tool engagement angle (which is defined as the width of cut, or step) is guaranteed to never be exceeded by the strategy.
The material is removed in spiral-like fashion. There are no sharp corners in the toolpath. Smoothness of the toolpath is precisely controlled by the dedicated parameters for the roughing rounding radius, the finishing radius and the linking radius. Linking is done preferably in the working plane with an additional small Z clearance, which helps fight heat buildup. The tool engages material using the so called 'Roll-In technique' which prolongs tool life. Both climb and mixed (climb and conventional) milling is available. For the mixed milling, the width of cut and the feed rate of conventional passes can be set separately from the climb passes.
How to choose the pocketing strategy
The choice number one is Adaptive This strategy is not set as default, only because it requires the additional licensing. So we strongly recommend purchasing it. All other variants must be tested only if this strategy is not available or gives the improper toolpath.
If Adaptive is not possible, and you need the even tool load, then try Deep HPC strategy.
If even tool load is not necessary and the machining step is more than 50% of the tool diameter then try HPC strategy
If even tool load is not necessary and the machining step is less than 50% then try Equidistant strategy.
Use Parallel strategy at your own discretion.
Use Equidistant (legacy) if all other strategies give improper toolpath.
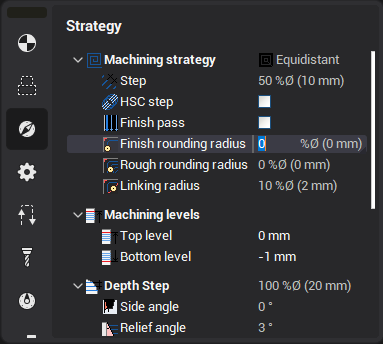
Tool path parameters
-
Back-off distance parameter
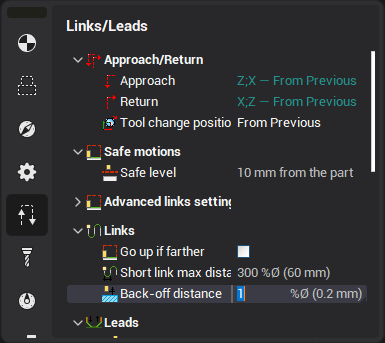
The tool can be lifted above the already machined surface when it moves to the next trochoidal arc start position.
-
Rounded links in zigzag mode
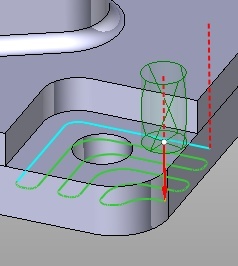
The ‘Finish rounding radius’, ‘Rough rounding radius’ and ‘Linking radius’ value is used for rounding of the links.
-
Links on the same Z-level
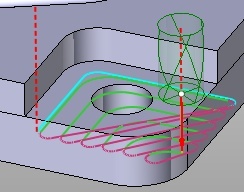
In the climb and conventional mode, the tool goes directly to the next path without retraction to the safe level. If a rapid motion is performed over an already machined surface, then the “Tool back-off distance” is used. “Idle radius” is also used to make the motion smooth.
-
Safe distance
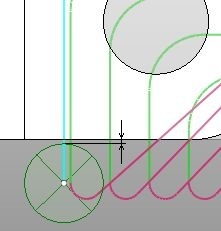
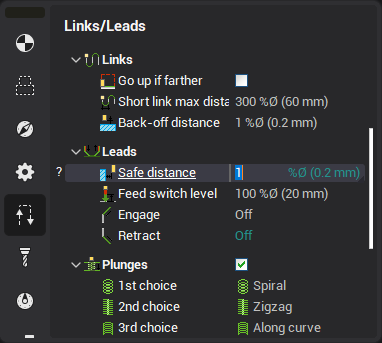
Safe distance is used to move the tool down/up from/to the safe surface.
The vertical motion is performed at this distance from the workpiece. So in version 10 there is no longer the need to enable the approaches/retractions to exclude the rapid feed collisions.
If you use a pre-drilled hole to plunge when roughing, the pre-drill tool diameter must be greater than the mill tool diameter by at least double the safe distance amount, otherwise the pre-drilled holes will not be detected .
-
Rapid feed links
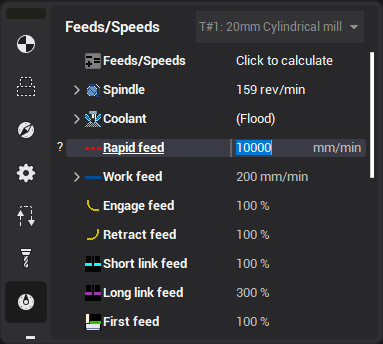
The link moves can be calculated using either the next feed or the return feed values. If the link length is less than the ‘short link’ distance, then the ‘next feed’ value is used, else the ‘return feed’ value is used. The return feed is set to 300% of the work feed by default, which is a non-cutting feed. If cutting is detected during a ‘return feed’ move when simulated, this move will be marked with an error.