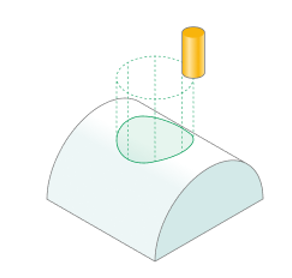
2D contouring
Application area:
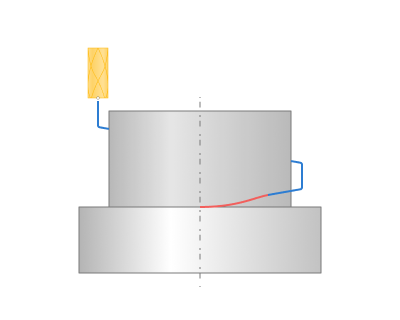
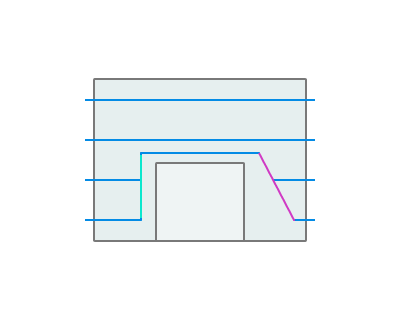
The operation is designed for machining along horizontal contours or curve projections on the horizontal plane, cylinder or figure of revolution. It is also possible machining with the cylindrical and polar interpolation. "Project on part" option using allow to get a complex five-axis toolpath, when orientation of the tool is changing. Operation in conjunction with the "Tool contact point" parameter allows you to easily machine chamfers on the parts. The operation's list of processes could consist of several contours and curve projections. Every object can have its own machining method: either the tool center passes along the contour or by touching it with the left or right of the tool. If the contour is machined from right or left, then it is possible to define an additional stock for it. Positive stock is laid off towards machining. If the center of the mill follows the contour, then the stock value will be ignored, for it is impossible to define exactly which side the additional stock should be laid off.
Setup:
The Setup tab is used to configure the primary parameters of the project. This can involve the positioning of the part on the equipment, the coordinate system of the part, and more. See more
Job assignment:
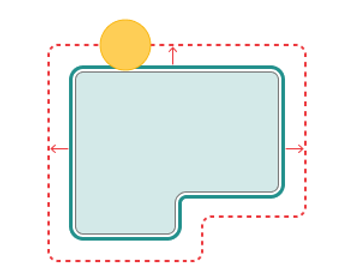
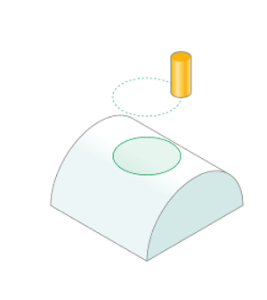
Base surface. This is the surface on which the trajectory is constructed according to the curve projected onto it . See more
Curve. Set work order along curve . See more
Pocket. A typical prismatic or turn-milling part consists of many simple shapes.To simplify this task, we can recognize the parts elements in a 3d model and automatically convert them to basic job assignment items, such as job zones and machining levels. See more
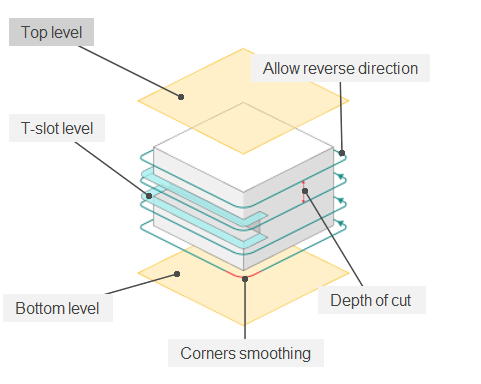
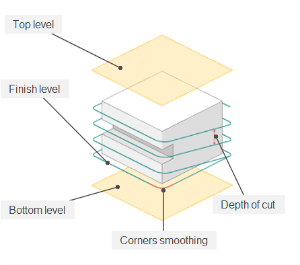
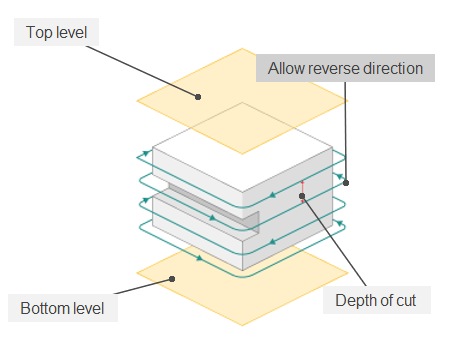
Top level. Specifying the top level by model elements. See more
Bottom level. Specifying the bottom level by model elements. See more
Add tabs. Adds tabs along the contour. See more
Properties. Displays the properties of an element. It is possible to add the stock. You can also call this menu by double clicking on an item in the list.
Delete. Removes an item from the list
Strategy:
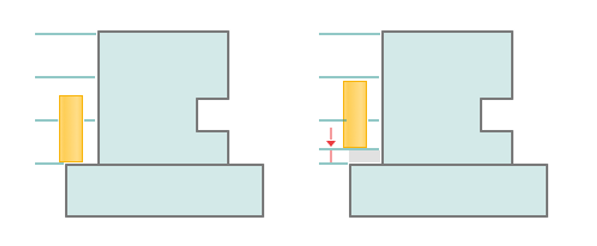
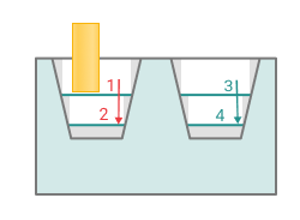
Depth of cut.
The material removed in a single pass along the tool axis between Top level and Bottom level. By default, it equals % of the cutting tool diameter.
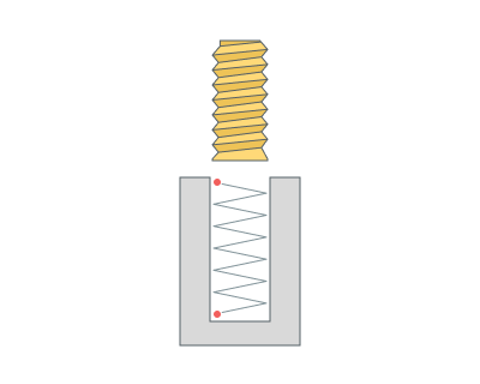
Helical machining.
Machining of a contour using a helical motion.
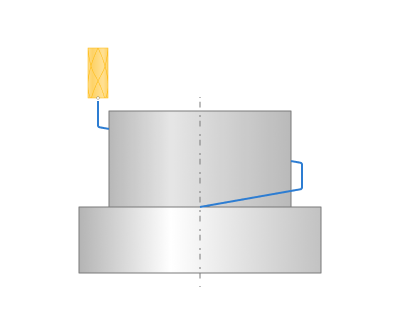
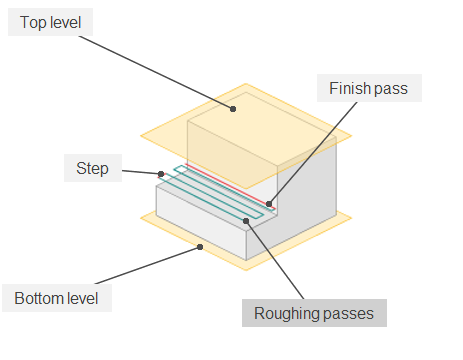
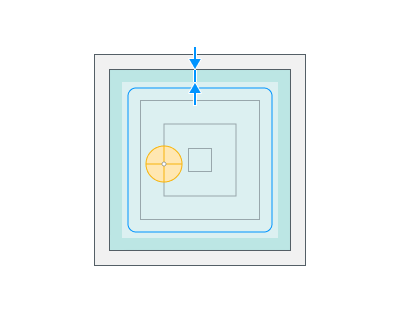
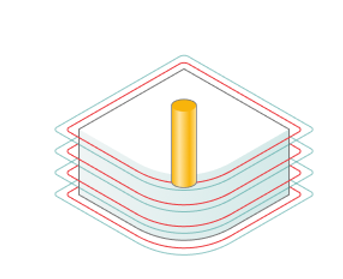
Roughining passes.
Toolpath is offset in plane by the 'Roughing passes' thickness amount. Additional passes are added to the contour by the value specified in the parameters with the specified number of steps.
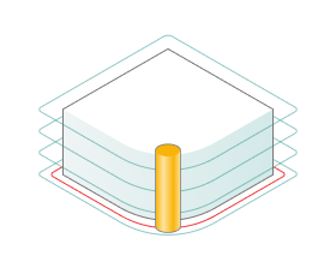
Finish pass.
The contour specified in the Job assignment becomes finishing. An additional roughing pass is added to it at a distance specified in the parameter.
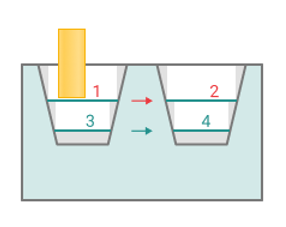
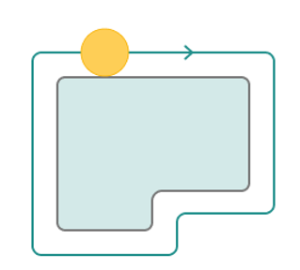
Sorting.
Controls the sequence of toolpath passes during the surface machining .
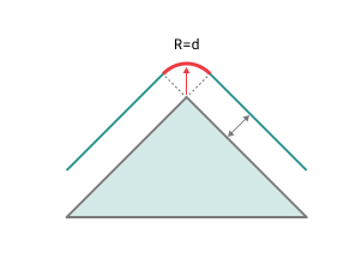
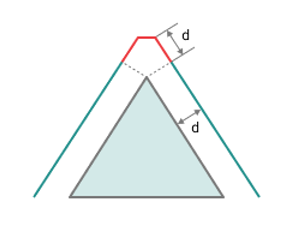
Corners smoothing.
When there is a sudden change of the tool direction, the milling control performs deceleration before starting the turn, and then accelerates again. This fact can lead to vibrations and high tool and milling machine wear. The problem can be solved if the toolpath has very few or no breaks. For this reason, in the system there is the toolpath smoothing function using the defined radius for machining inner or outer corners of the model.
Tabs.
Tabs are needed to hold the part or fragments of the workpiece from falling out at the final stage of processing, which can lead to tool breakage or defective parts.
Output.
Transformations.
A dialogue for transforming the toolpath.
Transformations:
Parameter's kit of operation, which allow to execute converting of coordinates for calculated within operation the trajectory of the tool. See more
See also:
Operation for 2/2.5-axes milling